Step 10
Let's create a script.js file with the following content and link it to the index.html.
const BASE_URL = "https://dataservice.accuweather.com";
const API_KEY = "USE_YOUR_API_KEY"; // terrible practice!
// You should never save API key directly in source code
const search = document.getElementById("search");
search.addEventListener("submit", getWeatherForecast);
function getWeatherForecast(event) {
event.preventDefault();
const city = document.getElementById("city").value.trim();
getLocationKey(city);
}
function getLocationKey(city) {
// TODO get the "location key" for the given `city`!
// then call getCurrentCondition to retrieve weather forecast for it!
}
function getCurrentCondition(location) {
// TODO get the "current condition" based on the `location` argument!
// then call updateUI to update the UI!
}
function updateUI(location, forecast) {
// TODO update the following based on `location` and `forecast` arguments!
document.getElementById("name").innerText = "City Name";
document.getElementById("condition").innerText = "Weather Condition";
document.getElementById("temperature").innerText = "Temperature";
}
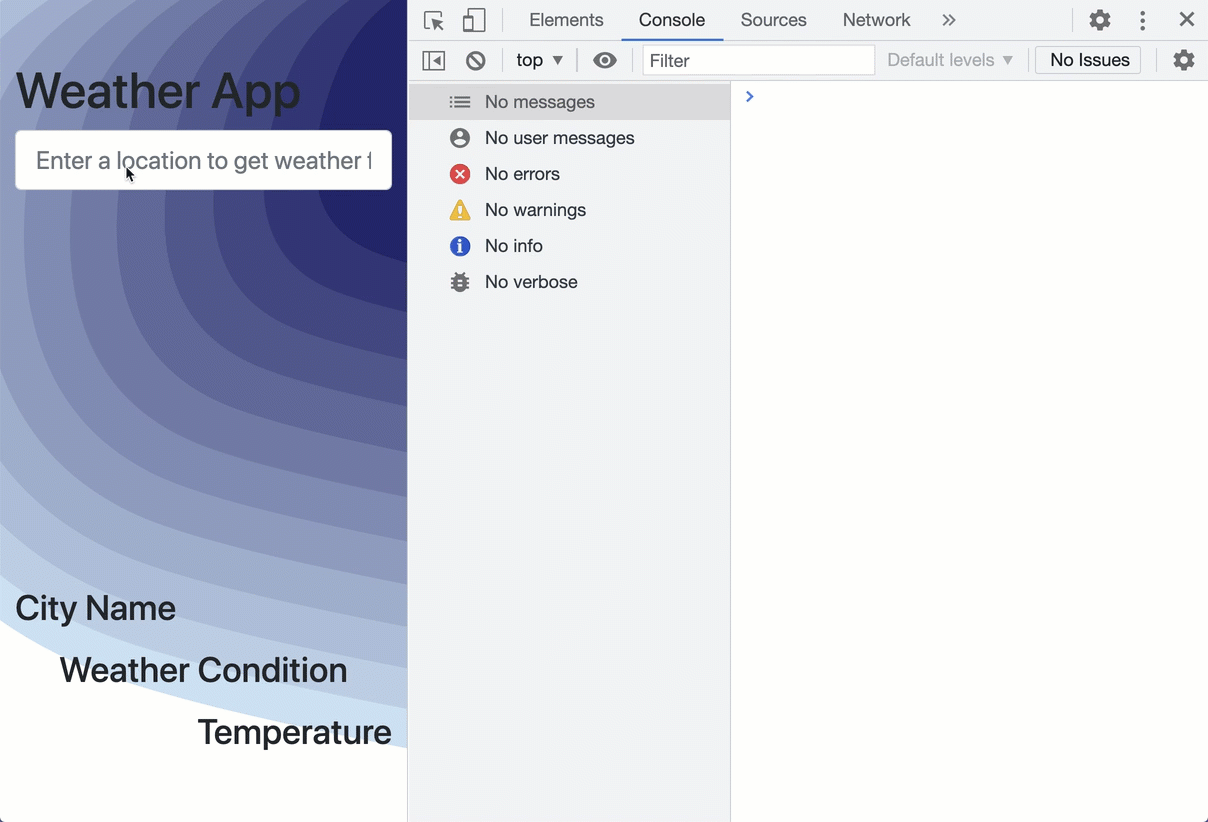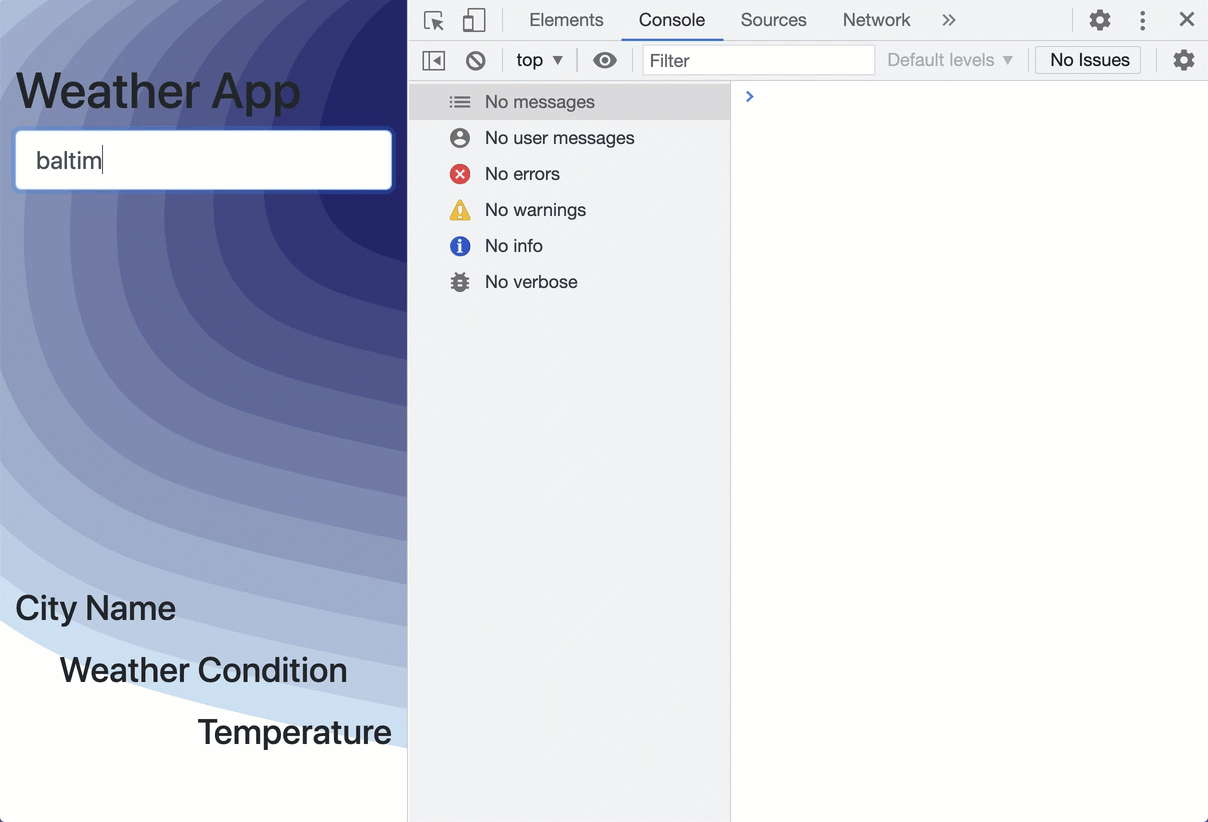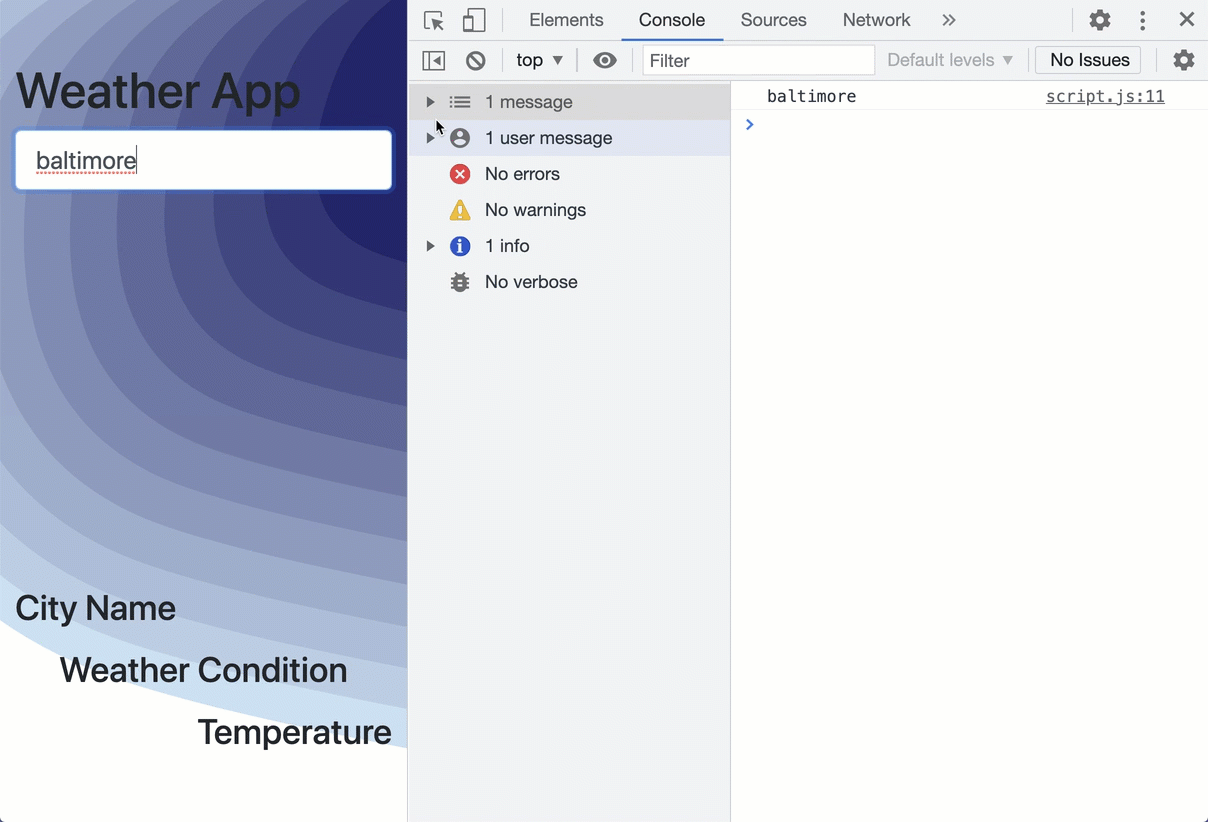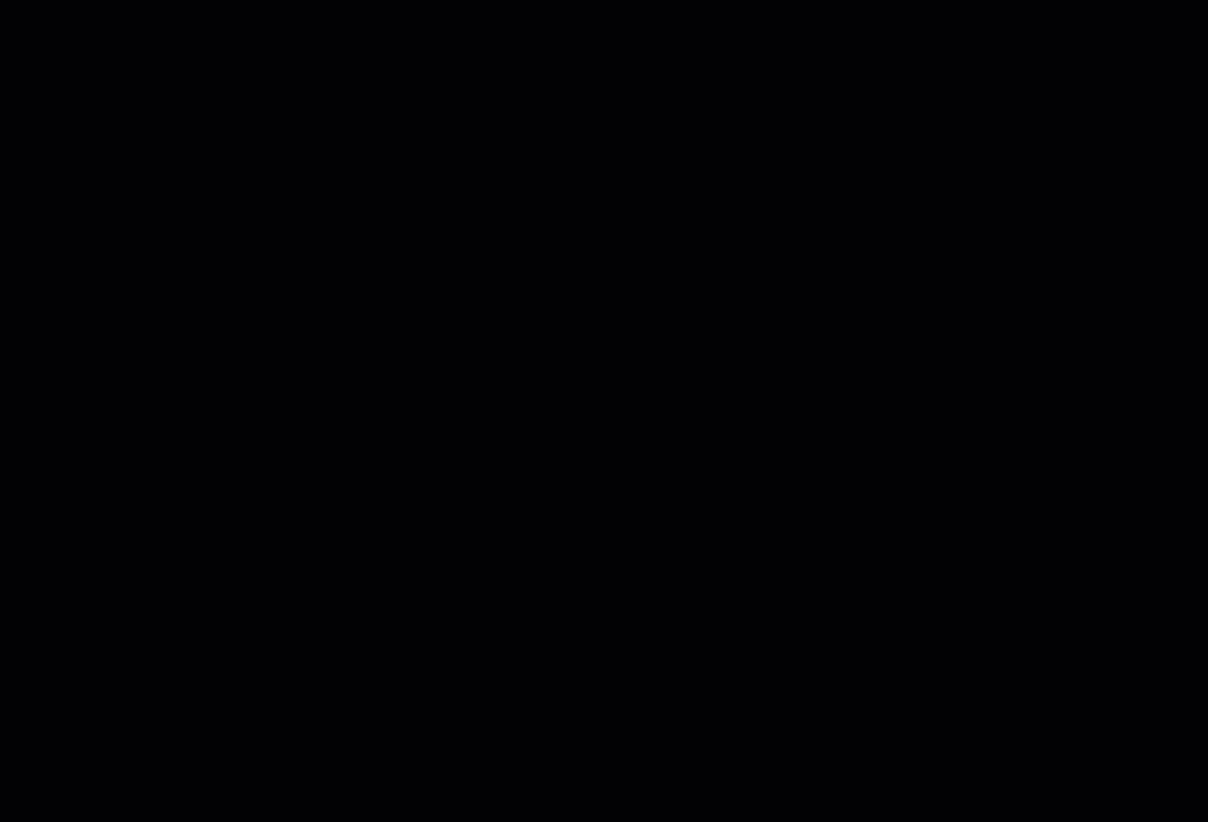
As you can see, the getWeatherForecast function is called when a user searches for a location.
For testing, you can have this method print the location to the console.